Resources
The iRRRd team has published a paper in the Child Development Perspectives Journal on ethical and culturally responsive biomarker research in the majority world
Do biomarkers have a place in human developmental research in the Majority World?
While commonly used in medicine, public health, and nutrition their application in developmental and educational science has remained contested.
In our new paper in Child Development Perspectives, we draw on both our own work and the field’s collective experience to examine the ethical considerations and practical challenges of conducting biomarker research responsibly in low-resource and conflict-affected settings in the Majority World.
We argue that, when implemented thoughtfully, biomarkers can meaningfully complement traditional developmental measures and deepen our understanding of how adversity becomes biologically embedded. The paper offers a roadmap for integrating biomarker data into developmental science while remaining grounded in ethics and cultural context.
Webinar en Español: “Quién cría a nuestros hijos, cómo el tiempo digital influye en aprender, jugar y crecer”
On January 9, 2026, our Director, Florencia Lopez Boo, joined a World Bank panel discussion “Quién cría a nuestros hijos, cómo el tiempo digital influye en aprender, jugar y crecer” as part of their broader initiative on early childhood education and digital environments, aiming to ground public debate and policy decisions in research rather than fear, hype, or one-size-fits-all prescriptions. Florencia Lopez Boo contributed an evidence-based perspective on young children’s learning and development in increasingly digital contexts.
The event convened researchers and policy leaders to examine how digital exposure is reshaping early childhood at home, in education systems, and across broader care environments in Latin America and the Caribbean.
The recording of the webinar “Quién cría a nuestros hijos, cómo el tiempo digital influye en aprender, jugar y crecer,” organized by The World Bank, is now available online.
Florencia Lopez Boo presented at an official side event of the 64th Session of the UN Commission for Social Development
On February 5, 2026 Florencia Lopez Boo, Director of Global TIES for Children, spoke on a virtual panel convened as an official side event of the 64th Session of the UN Commission for Social Development.
The discussion focused on how integrated social protection and early childhood care and education can better safeguard children’s rights and support more just and resilient societies, particularly in contexts of crisis and displacement. Florencia shared experiences from a collaboration between Global TIES for Children, GHESKIO, and IDB to pilot an adaptation of a remote early learning program for children in Haiti, whose school is often disrupted because of political violence and unrest.
Launching a new LEARN blog series: Get to Know a LEARN Scholar
Over the coming months, we’ll be sharing short profiles of the 20 scholars participating in LEARN, a global community of researchers and practitioners working at the intersection of early childhood development, systems change, and social justice. Every two weeks, we’ll spotlight one scholar’s path, questions, and work on the ground.
We’re pleased to kick off the series with Paola Balanta Cobo Mag. Psic - PhD, a Senior Interdisciplinary Researcher in Human Development, Education, and Rights and the field leader for the JUNTOS por la Prioridad Program in Colombia, a collaborative initiative focused on strengthening care systems and positioning early childhood development as a national and local priority.
Paola’s path into research was intentional and deeply rooted in lived experience. From an early age, she worked alongside families, children, and young people in communities shaped by inequality and armed conflict. Those experiences continue to inform the questions that drive her work today: how agency, resilience, and creativity are nurtured in vulnerable contexts.
Her research is intergenerational in nature and strongly emphasizes the promotion of exchange between youth, early childhood, and the pedagogical practices that exist at the intersection of institutional contexts. It sits at the intersection of psychology, education, and social justice - transforming everyday care and creativity into eco-pedagogies and community initiatives grounded in local resources, intergenerational relationships, and emotional co-regulation.
In our conversation, Paola reflects on how these early experiences shaped her research agenda and how they continue to guide her commitment to early childhood development and systems-level change.
The Play to Learn team has published a paper on Fathers’ Engagement with and perceptions of child play: Evidence from the Rohingya camps
Research on father engagement is heavily focused on Western families. Western-based programs to support fathers often do so in an individualistic manner, failing to address cultures in places where collective care is common. Limited existing research on fathers’ involvement in play emphasizes the influence of income and working status on fathers’ views on play. Overall, there is very little research on fathers' perceptions of play in refugee contexts, and there is no extensive study exploring this topic in the Rohingya context. In this context of forced displacement, we ask the following research question about the Rohingya fathers' perceptions of play.
Research Question:
How do fathers perceive children’s play in both structured (Humanitarian Play Labs) as well as unstructured (home and surrounding areas) play settings in the Rohingya camps in Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh?
The iRRRd team has published a paper on Predictors of antenatal care utilization among the Rohingya population in the refugee camps of Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh
We're excited that the latest article from our iRRRd prenatal birth cohort in Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh is now out! See the post below for details. This paper adds important evidence on maternal health care access in humanitarian settings, drawing on data from our ongoing study in Cox's Bazar.
The paper reflects a close collaboration between early-career scholars, senior researchers, and field teams, and highlights how context-specific constraints—particularly mobility and timing—shape antenatal care use even where services are widely available.
Congratulations to Daniel Simon, Duja Michael, @Md. Sajjadur Rahman, Caroline Hiott, AK Rahim, Kazi Istiaque Sanin, Fahmida Tofail, Alice Wuermli and everyone who contributed to this work.
We’re glad to see this paper out in the world and contributing to ongoing conversations about how to strengthen maternal health systems for displaced and crisis-affected populations.
Global TIES Fellowship in Buenos Aires: Applications Now Open
We are pleased to announce the launch of the Global TIES Fellowship in Buenos Aires, a new experiential learning program developed in collaboration with NYU Buenos Aires and NYU Steinhardt.
Florencia Lopez Boo presented at an event on Neuroscience and Education for the Future: Challenges and Opportunities in the Latin-America Region
On December 9, 2025 our Director, Florencia Lopez Boo, joined “Neurociencia y Educación para el Futuro: Desafíos y oportunidades en la región,” (“Neuroscience and Education for the Future: Challenges and Opportunities in the Latin-America Region”) an event organized by the School of Education at Universidad de 'San Andrés'. Florencia presented about how neuroscience can inform public policies in education and - along with Sebastian J. Lipina, Diego Golembek, and Ezequiel Gomez Caride - contributed to a broader discussion on the challenges and opportunities for the neuroscience of education. The event brought together teachers, school directors, scholars and practitioners examining how neuroscience can inform education systems across Latin America. In her remarks, she noted that while nudges opened the door for behavioral science in policymaking, a neuroscientific approach represents a deeper shift in how policy can improve people’s lives. We are grateful to UDESA for convening this timely conversation and for inviting Global TIES for Children to engage with colleagues across the region on the future of education.
Florencia Lopez Boo presented at the Inaugural Nutrition & Early Years Advisory Group (NEYAG)
Congratulations to all those involved in launching the Nutrition & Early Years Advisory Group (NEYAG), which was inaugurated on December 4, 2025 at a meeting titled: “Shaping the Future of Africa: Nutrition and Early Childhood Development as Game Changers.”
Hosted in Dakar by the World Bank and partners, the meeting brought together leaders across sectors to advance strategies that strengthen human capital through improved nutrition and early childhood development.
At the event today, our Director, Florencia Lopez Boo, shared insights from Global TIES for Children’s research portfolio on how to integrate health, nutrition, and child development policies, highlighting evidence on what policy environment is needed to enable such integration and what governance structures and regulations can inform impactful, scalable policies across the continent.
Hirokazu Yoshikawa Awarded the 2025 Klaus J. Jacobs Research Prize
The award recognizes his pioneering research on the ways public policies and programs, particularly in early childhood and immigration, shape human development.
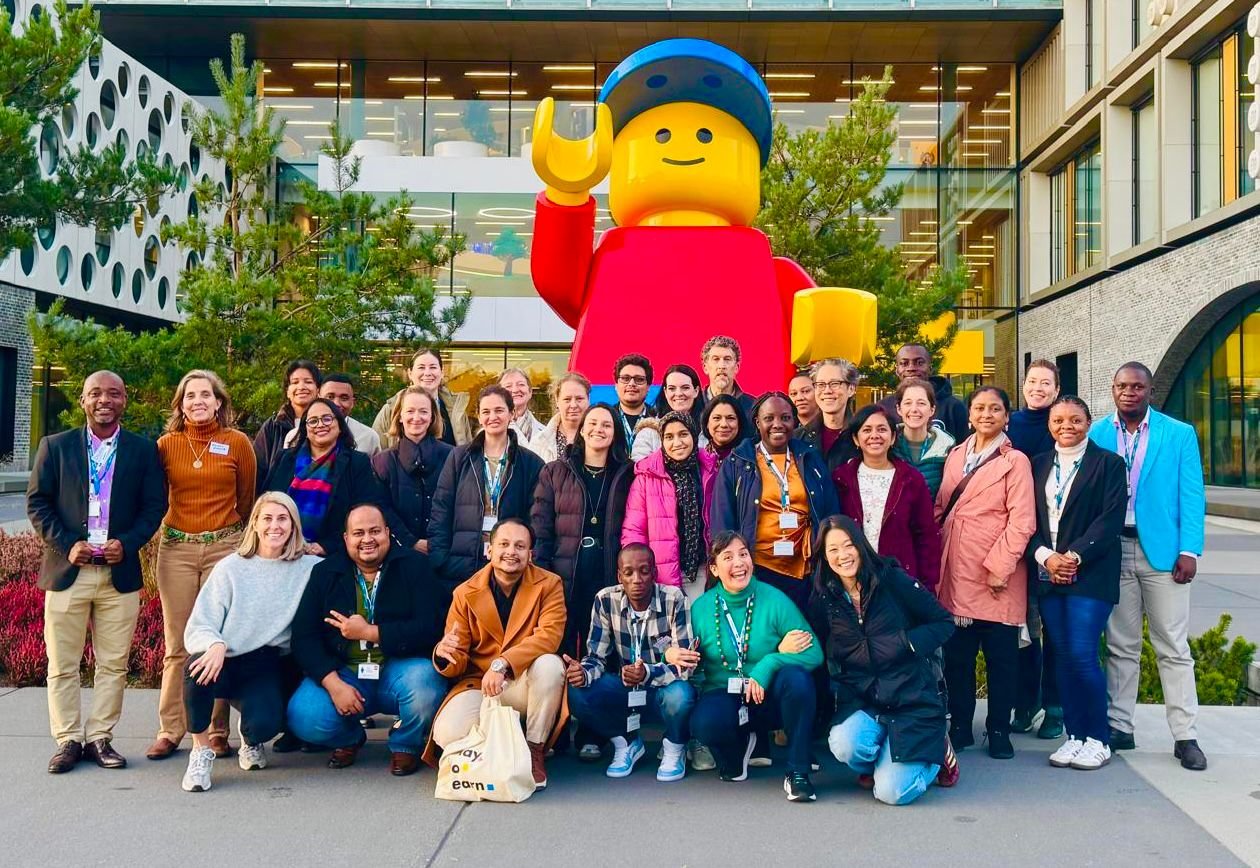
Engage team members participate in the project’s final Comunity of Practice convening
From November 3-6, 2025, Hirokazu Yoshikawa and Sharon Kim represented Global TIES for Children at the final Engage Community of Practice convening, organized by EDC and hosted at the LEGO Foundation headquarters in Billund, Denmark.
Over three days, partners from across the Engage portfolio shared evidence and lessons on strengthening student engagement in early childhood and primary education across diverse contexts.
The sessions focused on:
Insights from implementing and adapting the Engage tools
Trends emerging across countries and developmental levels
How data can drive program improvement and system-level change
This convening wasn’t a “show-and-tell.” It was hands-on, reflective, and honest about what it takes to embed child-centered, playful learning approaches into teaching and learning systems—and sustain them.
Carolina Rivas released a new book titled: (Dis)connected? Digital Public Services and the Challenge of Equity, in collaboration with the IDB
We’re proud to celebrate our colleague Carolina Rivas, Senior Research Associate at Global TIES for Children (NYU), on the release of her new book, in collaboration with the Inter-American Development Bank.
Based on 22,000+ in-person surveys across 11 countries, interviews with public officials, and detailed reviews of government digital platforms, the book examines whether digitalization of public services is increasing access — or widening existing gaps.
Key takeaway:
Digital systems can improve efficiency, but not everyone gets the benefits. Without intentional policy and design choices, digitalization risks deepening regional inequities.
During the launch event in Washington, D.C., Carolina and co-author Julieth Santamaria presented the findings, followed by a panel discussion on what governments can do to ensure digital transformation leaves no one behind.
The iRRRd team has published their first paper on their ongoing pre-natal birth cohort study in Bangladesh
We’re proud to share the work of our NYU-TIES colleague, Alice Wuermli, and her coauthors, who have just published the first major paper of their ongoing pre-natal birth cohort study in Bangladesh.
This cohort profile paper outlines the study's foundations, sets the stage for future publications, and offers a powerful reminder of why early childhood research matters—not just for developmental science, but for creating real-world impact in diverse contexts. At Global TIES we are committed to bridging rigorous evidence with meaningful action.
Read Alice’s post to learn more about the study’s insights and the implications they hold for early childhood initiatives. Kudos to Alice and the entire research team for their hard work and dedication.
Florencia Lopez Boo presented at the IDB Regional Policy Dialogue: Transforming Early Childhood Development in Latin America & Caribbean
Florencia Lopez Boo presented at the 2025 Inter-American Development Bank Regional Policy Dialogue: "Childhood, Innovation, Impact: Transforming Early Childhood Development in Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC)" in Mexico City.
More than 100 participants, including authorities from 17 LAC countries, donors, civil society, and academics.
Wonderful speakers and panelists such as Susan Walker, Mariano Bosch Mossi, Marta Rubio-Codina, Carolina Freire, Romina Tome, Alexandre Bagolle, Claudia Vazquez, Jorge Gaete, Filipa de Castro, Eunice Deras, Andrés Moya, among many others.
Tremendous master lecture by James Cairns.
And a first-class closure of the "Child Development Innovation Fund."
Not only was it motivating to discuss the challenges of Latin America in the coming years, it was also nice to catch up with the Haiti and Argentina teams whom we are working on border agendas, and to see so many dear friends and colleagues. Congratulations to the Pablo Ibarraran team and the Inter-American Development Bank for this unique space for reflection.
The iRRRd Longitudinal team has launched training for the pilot phase of the 36-month follow up
We’re excited to share that we kicked off training for the pilot phase of our iRRRd study on October 5, together with our partners at icddr,b and University of California, Davis. Over the next three months, we will test new measures for the next wave of data collection with Rohingya refugee families living in the southeast of Bangladesh.
This wave — following children in our study cohort as they reach three years of age — has been made possible by a $𝟯 𝗺𝗶𝗹𝗹𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗴𝗿𝗮𝗻𝘁 𝗳𝗿𝗼𝗺 The LEGO Foundation.
“This pilot is a critical step to make sure our tools capture the unique realities of Rohingya and host community families,” said Fahmida Tofail, co-Principal Investigator and Scientist at icddr,b. “We are eager to generate insights that can inform both science and policy.”
“Having the chance to follow children into toddlerhood is an extraordinary opportunity,” added Alice Wuermli, Principal Investigator for iRRRd and Director of Research & Innovation at NYU Global TIES for Children. “It allows us to investigate the mechanisms — from the molecular to the social — of how pre- and postnatal environments affect early development.”
𝗪𝗲 𝗮𝗿𝗲 𝗱𝗲𝗲𝗽𝗹𝘆 𝗴𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗲𝗳𝘂𝗹 𝘁𝗼 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗟𝗘𝗚𝗢 𝗙𝗼𝘂𝗻𝗱𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻, 𝗶𝗰𝗱𝗱𝗿,𝗯, 𝗨𝗖 𝗗𝗮𝘃𝗶𝘀, 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗮𝗯𝗼𝘃𝗲 𝗮𝗹𝗹, 𝘁𝗼 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗳𝗮𝗺𝗶𝗹𝗶𝗲𝘀 𝘄𝗵𝗼 𝗺𝗮𝗸𝗲 𝘁𝗵𝗶𝘀 𝘄𝗼𝗿𝗸 𝗽𝗼𝘀𝘀𝗶𝗯𝗹𝗲.
Prof. Hirokazu Yoshikawa participated in the launch of a new global research partnership to study the Tirana School Street model
Prof. Yoshikawa participated in the launch of a new global research partnership with Epoka University School of Architecture and Planning to study the Tirana School Street model.
Global TIES, The Agency Fund & NYU Office of the Provost co-hosted The Agency Summit
The Global TIES team was proud to co-host on NYU’s campus, The Agency Summit with The Agency Fund and NYU Office of the Provost. Organized alongside #UNGA week here in New York City, The Agency Summit on Friday, September 26th, was designed to “foster collaboration between researchers, practitioners, and funders to explore how personal and collective agency can be harnessed to promote sustainable development outcome.”
The full-day agenda was opened by heavy-hitters Hazel Markus, Karla Hoff, and Joseph E. Stiglitz, and included many engaging conversations.
In a day full of standout moments, we want to highlight the “Practice” panel with Tarun Cherukuri, Amanda Beatty, Carolina Trivelli Avila, and Hirokazu Yoshikawa (moderated by our very own Florencia Lopez Boo): a grounded conversation on turning evidence into decisions that communities can actually use.
We loved Kate Schwartz’s reflections on implementation, measuring what matters, building feedback loops, and staying close to context.
Prof. Hirokazu Yoshikawa presented Engage tools at UKFIET alongside the LEGO team
Our very own Hirokazu Yoshikawa presented alongside the The LEGO Foundation Engage research team from South Africa, Colombia, Bangladesh, Sierra Leone, Uganda, Denmark to a packed room.
The symposium showcased findings from a global research partnership using the Engage observation tool, now in its 6th year of development. This innovative toolkit measures how adults support children’s engagement in learning – at home and in classrooms – across four dimensions: Exploration, Agency, Social & personal connection, Emotional climate.
The results are powerful: engagement not only boosts academic skills, but also supports social and emotional learning. Insights like these are shaping how we measure adult–child interactions and design programs that better support children’s learning across the early years and primary school.